- Quitmate
- VERIFICATION OF IDENTITY and ONLINE POLICE CHECKS
- MedAdvisor
- Urgent Medication Delivery
- NDSS and Diabetic Supplies
- Blood Pressure Check
- Webster Packing
- Vaccination
- Absent from Work Certificate
- Medication Disposal Services
- Equipment Hire
- Ear Piercing
- HUBBED
- Australia Post
- Passport and ID Photo’s
- SUPERVISED RAPID ANTIGEN TEST
- Simple Compounding
- Compression Garment Supply & Advice
- Consumer Medicines Information
- Home Deliveries
- Inhaler Technique Assistance
- MedsChecks
- Mental Health Support
- Quit Smoking Support
- Script on file Reordering Service
- Witnessing Documents or Statutory Declarations
- Wound Management
Understanding the 3 Main Types of Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Options
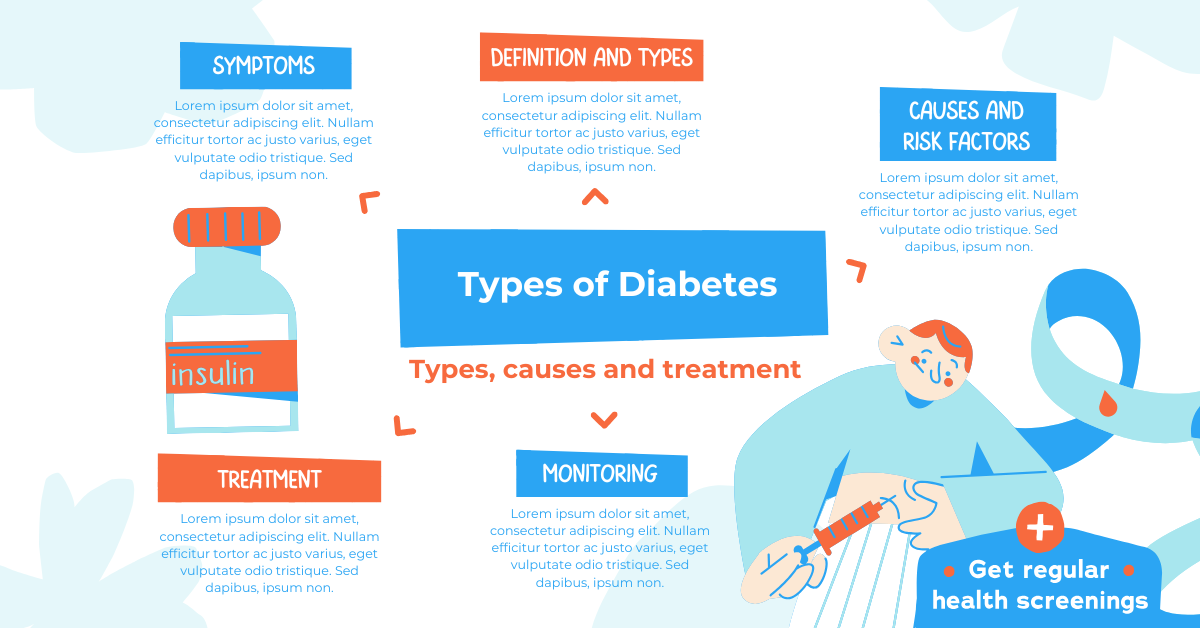
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). With millions of Australians living with diabetes, understanding the different types of diabetes is crucial for early detection, effective management, and long-term health.
In this guide, we’ll explore the three main types of diabetes—Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes—including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Whether you or someone you love is managing diabetes or at risk, this blog will give you a clear and helpful overview.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your body is unable to produce or properly use insulin—a hormone that regulates glucose levels in the blood. If left unmanaged, high blood sugar can lead to serious health complications including nerve damage, heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems.
The Main Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
- Cause: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Who it affects: Commonly diagnosed in children and young adults but can develop at any age.
- Symptoms: Sudden weight loss, frequent urination, extreme thirst, fatigue.
- Treatment: Daily insulin injections or use of an insulin pump, blood sugar monitoring, healthy diet.
Type 1 diabetes is not preventable and requires lifelong insulin therapy and management.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
- Cause: The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it.
- Who it affects: More common in adults over 40, but increasing among younger people due to lifestyle factors.
- Symptoms: Can be subtle and develop slowly—fatigue, frequent infections, blurred vision.
- Treatment: Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), oral medications, and in some cases, insulin therapy.
📝 Tip: Early diagnosis can significantly improve health outcomes. Learn more about the warning signs of diabetes in our detailed guide.
3. Gestational Diabetes
- Cause: Hormonal changes during pregnancy affect insulin function.
- Who it affects: Pregnant women, typically diagnosed during the second or third trimester.
- Symptoms: Often no noticeable symptoms—routine screening during pregnancy is essential.
- Treatment: Healthy eating, regular exercise, blood sugar monitoring, and sometimes insulin.
Gestational diabetes usually disappears after childbirth, but it increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Risk Factors Across All Types
- Family history of diabetes
- Being overweight or obese
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High blood pressure
- Poor diet
- Gestational diabetes in previous pregnancy
Managing Diabetes with Taylor’s Pharmacy
At Taylor’s Pharmacy, we’re here to support you every step of the way. From blood glucose monitors and insulin supplies to nutritional supplements, our knowledgeable team can help you manage diabetes with confidence.
We also offer:
- Medication reviews
- Blood pressure checks
- Health advice tailored to your needs
Whether you’re newly diagnosed or managing diabetes long-term, we provide the diabetes supplies and needs and expertise to help you stay in control.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the types of diabetes is the first step toward better health. From Type 1 and Type 2 to gestational diabetes, each requires a unique approach to management and care. Recognising early symptoms and seeking timely support can make all the difference in living a full, active life.
Don’t forget to read our blog on the warning signs of diabetes to stay informed and proactive about your health.

